Cloud cover
From Conservapedia
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by DavidB4-bot (Talk | contribs) at 05:24, September 9, 2018. It may differ significantly from current revision.
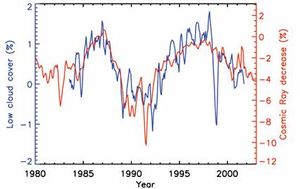
Correlation between cosmic rays and cloud cover
Cloud cover is a sorely neglected factor in debates over global warming. Cosmic rays from space influence the Earth’s climate by affecting cloud formation in the lower atmosphere.[1] In fact, cosmic rays and cloud cover are so closely correlated as to suggest a cause and effect relationship.
- ... most scientists believe that an increase in low cloud cover may cause a net cooling in the atmosphere because of an increased albedo, while an increase in high clouds may cause the atmosphere to warm, as high clouds act as a "blanket" and reflect infrared radiation back to the earth.[2]
Richard Lindzen wrote:
- Cloud cover in models is poorly treated and inaccurately predicted. Yet clouds reflect about seventy-five watts per square meter. Given that a doubling of carbon dioxide would change the surface heat flux by only two watts per square meter, it is evident that a small change in cloud cover can strongly affect the response to carbon dioxide. ... the effects of clouds in reflecting light and in enhancing the greenhouse effect are roughly in balance.[3]