Difference between revisions of "North America"
DavidB4-bot (Talk | contribs) (→Topography: clean up & uniformity) |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 26 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''North America''' is the land mass consisting of [[ | + | [[Image:North america pol97.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Political boundaries of North America]] |
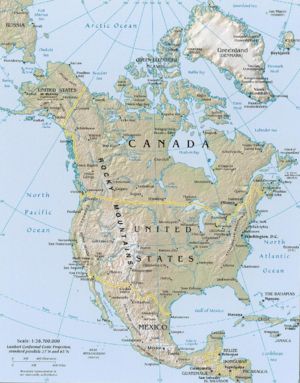
| + | [[Image:North america ref02.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Shaded relief of North America]] | ||
| + | '''North America''' is the continental land mass of the Western Hemisphere consisting of [[Bermuda]], [[Canada]], the [[United States of America]], [[Greenland]] and [[Saint Pierre and Miquelon]]. It may also include [[Mexico]], the seven countries of [[Central America]], and many of the islands of the [[Caribbean Sea]]. North America is bounded on the north by the [[Arctic Ocean]], the east by the [[Atlantic Ocean]], the south by the Caribbean Sea and [[South America]], and the [[Pacific Ocean]] to the west. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The name ''America'' derives from Italian explorer and navigator [[Amerigo Vespucci]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: the term "North American" in some contexts refers only to the US and Canada (see ''[[norteamericano]]''). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Land== | ||
| + | North America has an area of 9.2 million square miles, ranking it third in size among the seven continents. Between Nordost Rundingen in Greenland to Attu Island, Alaska, it spans across 176° of longitude, with the bulk of the landmass north of 30° latitude. | ||
| + | |||
| + | North America's coastline is irregular and indented with bays, the largest of which are Hudson Bay in Canada, the Gulf of Mexico, the Gulf of Alaska, and the Sea of Cortez between the peninsula Baja California and the Mexican mainland. Large islands are immediately offshore in northern Canada, including Victoria, Ellesmere, Baffin, and Greenland, the world's largest island. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/recenteqsww/Maps/region/N_America.php See latest [[Earthquake]]es.] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Topography=== | ||
| + | North America is considered to be divided into five major regions: | ||
| + | *The [[Canadian Shield]], an extensive plateau comprising much of [[Greenland]], the eastern half of Canada, and the [[Great Lakes]] area, with an underlayment of ancient crystalline rocks. | ||
| + | *The [[Coastal Plain]], of the eastern United States and Mexico. | ||
| + | *The [[Appalachian Mountains]]. | ||
| + | *The [[Central Lowland]], situated between the Appalachians and the [[Continental Divide]] and containing the Great Plains of the United States and Canada. | ||
| + | *The western region, which includes the major mountain ranges from [[Alaska]] to Mexico and the [[Great Basin]]. Within this region is the highest point on the continent, Alaska's [[Denali]] (formerly known as [[Mt. McKinley]]) (20,320 ft), and the lowest point in the [[Western Hemisphere]], [[Death Valley]] (282 ft below sea level) in [[California]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Climate=== | ||
| + | Only the eastern two-thirds of the United States and southern Canada have climate conditions in which all four seasons are present. Northern Canada, Alaska, and Greenland contain arctic and sub-arctic climates characterized by very brief summers and extremely cold winters; snow and ice are present much of the year, and in the area north of the Arctic Circle much of the land bears permafrost under the soil. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Drainage=== | ||
| + | ===Flora=== | ||
| + | ===Fauna=== | ||
| + | ===Resources=== | ||
| + | ===Arable land=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==People== | ||
| + | ===Ethnic groups=== | ||
| + | ===Languages=== | ||
| + | ===Religion=== | ||
| + | ===Education=== | ||
| + | ===Health=== | ||
| + | ===Demography=== | ||
| + | ==Economy and Commerce== | ||
| + | ===Industry=== | ||
| + | ===Agriculture=== | ||
| + | ===Forestry=== | ||
| + | ===Fishing=== | ||
| + | ===Transportation=== | ||
| + | ===Trade=== | ||
| + | == History == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Continents]] | [[Category:Continents]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Regions of the World]] | ||
| + | [[Category:North America]] | ||
Revision as of 16:47, July 13, 2016
North America is the continental land mass of the Western Hemisphere consisting of Bermuda, Canada, the United States of America, Greenland and Saint Pierre and Miquelon. It may also include Mexico, the seven countries of Central America, and many of the islands of the Caribbean Sea. North America is bounded on the north by the Arctic Ocean, the east by the Atlantic Ocean, the south by the Caribbean Sea and South America, and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
The name America derives from Italian explorer and navigator Amerigo Vespucci.
Note: the term "North American" in some contexts refers only to the US and Canada (see norteamericano).
Contents
Land
North America has an area of 9.2 million square miles, ranking it third in size among the seven continents. Between Nordost Rundingen in Greenland to Attu Island, Alaska, it spans across 176° of longitude, with the bulk of the landmass north of 30° latitude.
North America's coastline is irregular and indented with bays, the largest of which are Hudson Bay in Canada, the Gulf of Mexico, the Gulf of Alaska, and the Sea of Cortez between the peninsula Baja California and the Mexican mainland. Large islands are immediately offshore in northern Canada, including Victoria, Ellesmere, Baffin, and Greenland, the world's largest island.
Topography
North America is considered to be divided into five major regions:
- The Canadian Shield, an extensive plateau comprising much of Greenland, the eastern half of Canada, and the Great Lakes area, with an underlayment of ancient crystalline rocks.
- The Coastal Plain, of the eastern United States and Mexico.
- The Appalachian Mountains.
- The Central Lowland, situated between the Appalachians and the Continental Divide and containing the Great Plains of the United States and Canada.
- The western region, which includes the major mountain ranges from Alaska to Mexico and the Great Basin. Within this region is the highest point on the continent, Alaska's Denali (formerly known as Mt. McKinley) (20,320 ft), and the lowest point in the Western Hemisphere, Death Valley (282 ft below sea level) in California.
Climate
Only the eastern two-thirds of the United States and southern Canada have climate conditions in which all four seasons are present. Northern Canada, Alaska, and Greenland contain arctic and sub-arctic climates characterized by very brief summers and extremely cold winters; snow and ice are present much of the year, and in the area north of the Arctic Circle much of the land bears permafrost under the soil.