Difference between revisions of "Planck's constant"
m (added ca year Planck introduced the Planck constant) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Planck's constant''' | + | '''Planck's constant''', denoted <math>h</math>, is a fundamental constant in [[physics]]. The current value of '''Planck's constant''' is <math>6.626070040(81) \times 10^{-34}</math> Joule-seconds (numbers in brackets represent uncertainty in the last two decimal places).<ref>http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?h</ref> |
| − | + | ==History== | |
| − | + | It was first used by [[Max Planck]] around 1900 to explain the radiation curves of black-bodies. He supposed that [[light]] could be modelled as a series of particles (now called [[photons]]), each with an [[energy]] proportional to its frequnecy, <math>\nu</math>. The constant of proportionality was Planck's constant. Mathematically this can be expressed as: | |
| − | + | <math>E = h \nu</math> | |
| − | [[ | + | |
| + | In 1924, Louis De Broglie proposed [[Wave-particle duality]], the idea that matter ([[proton]]s and [[electron]]s for example) had a wave-like nature.<ref>https://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1929/broglie-bio.html</ref> Here too, is Planck's constant: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\lambda = \frac{h}{p} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where | ||
| + | :<math>\lambda</math> is the [[wavelength]] of the particle | ||
| + | :<math>p</math> is the [[momentum]] of the particle | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Planck constant also occurs in equations fundamental to [[quantum mechanics]], such as the [[Schrodinger equation]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Reduced Planck's Constant== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Planck's constant often occurs in equations with the mathematical constant <math>\pi</math>. As such, a factor of <math>\frac{1}{2 \pi}</math> may be taken into Planck's constant as | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\hbar = \frac{h}{2 \pi}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The resulting constant is pronounced "h-bar". | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | *[[Quantum mechanics]] | ||
| + | *[[Photon]] | ||
| + | *[[Schrodinger equation]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | {{Reflist}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Physics]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Quantum Mechanics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:39, June 6, 2021
Planck's constant, denoted 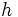 , is a fundamental constant in physics. The current value of Planck's constant is
, is a fundamental constant in physics. The current value of Planck's constant is  Joule-seconds (numbers in brackets represent uncertainty in the last two decimal places).[1]
Joule-seconds (numbers in brackets represent uncertainty in the last two decimal places).[1]
History
It was first used by Max Planck around 1900 to explain the radiation curves of black-bodies. He supposed that light could be modelled as a series of particles (now called photons), each with an energy proportional to its frequnecy,  . The constant of proportionality was Planck's constant. Mathematically this can be expressed as:
. The constant of proportionality was Planck's constant. Mathematically this can be expressed as:

In 1924, Louis De Broglie proposed Wave-particle duality, the idea that matter (protons and electrons for example) had a wave-like nature.[2] Here too, is Planck's constant:

where
 is the wavelength of the particle
is the wavelength of the particle is the momentum of the particle
is the momentum of the particle
The Planck constant also occurs in equations fundamental to quantum mechanics, such as the Schrodinger equation.
Reduced Planck's Constant
Planck's constant often occurs in equations with the mathematical constant  . As such, a factor of
. As such, a factor of  may be taken into Planck's constant as
may be taken into Planck's constant as

The resulting constant is pronounced "h-bar".