Difference between revisions of "Human evolution"
From Conservapedia
m (added pic) |
m (added pic) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| 2.4 - 1.5 mya | | 2.4 - 1.5 mya | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Homo erectus.png|125px|center]] |
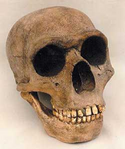
| ''[[Homo erectus]]'' | | ''[[Homo erectus]]'' | ||
| - | | - | ||
Revision as of 18:06, June 5, 2009
Human evolution or paleoanthropology is a theory within evolution which posits that mankind evolved from more primitive species over the course of 40 million years, with the most dramatic changes occuring during the last 2 million years. An absence of intermediary fossils, no plausible pathway for the development of the brain, and countless other disproofs to the theory has rendered human evolution more of a philosophy of a belief system rather than a valid scientific concept.
| Claimed chain of early humans/hominids according to evolutionary science | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Image | Species | Details | Claimed Dates |
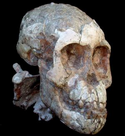
| Ardipithecus ramidus | Earliest claimed fossil hominid. | 4.4 mya | |
| Australopithecus anamensis | Found in Allia Bay in Kenya, and named in 1995. | 4.2 - 3.9 mya | |
| Australopithecus afarensis | - | 3.5 - 2.9 mya | |
| Homo habilis | Called handy man due to tools found near his remains | 2.4 - 1.5 mya | |
| Homo erectus | - | 1.8 mya - 300,000 years ago | |
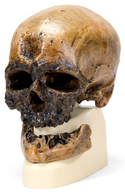
| Homo sapiens (archaic) | - | 500,000 - 200,000 years ago | |
| Homo sapiens neanderthalensis | - | 230,000 - 30,000 years ago | |
| - | Homo sapiens (modern) | - | 120,000 years ago - present |