Difference between revisions of "Axon"
From Conservapedia
m (Reverted edits by Mariowhaa (Talk); changed back to last version by Tmtoulouse) |
DavidB4-bot (Talk | contribs) (clean up) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
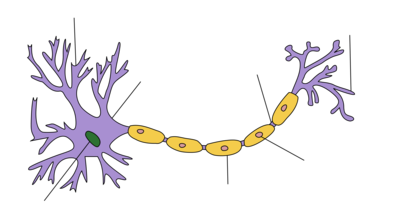
| − | An '''axon''' or '''nerve fiber''' is one of the three primary parts of a [[neuron]]. It is an extension that grows away from the [[soma]] or cell body and is used to propagate an [[electrical impulse]] from one neuron to another as a means of communication. Axons are often bundled together in groups called [[nerves]]. These nerves are the transmission lines that move information through the body. The axon has several major anatomical parts: the [[Axon hillock]], the [[Axon initial segment]], the [[ | + | {{Neuron map|Axon}}An '''axon''' or '''nerve fiber''' is one of the three primary parts of a [[neuron]]. The word comes from the Greek άξονα "axona", meaning "line" or "axis". It is an extension that grows away from the [[soma]] or cell body and is used to propagate an [[electrical impulse]] from one neuron to another as a means of communication. Axons are often bundled together in groups called [[nerves]]. These nerves are the transmission lines that move information through the body. The axon has several major anatomical parts: the [[Axon hillock]], the [[Axon initial segment]], the [[myelin]]ated portions, and the unmyelinated portions referred to as the [[Node of Ranvier]]. |
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
* Kandel, ER; Schwartz JH, Jessell TM (2000). Principles of Neural Science, 4th ed., New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-8385-7701-6. | * Kandel, ER; Schwartz JH, Jessell TM (2000). Principles of Neural Science, 4th ed., New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-8385-7701-6. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Biology]] | [[Category:Biology]] | ||
[[Category:Neuroscience]] | [[Category:Neuroscience]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:12, June 23, 2016
| Axon |
|---|
References
- Martin, JH (2003). Neuroanatomy text and atlas 3rd ed., New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Kandel, ER; Schwartz JH, Jessell TM (2000). Principles of Neural Science, 4th ed., New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-8385-7701-6.