Difference between revisions of "Bernoulli experiment"
From Conservapedia
m (→Expectation and Variance: spelling) |
(→Expectation and Variance) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
The variance is <math>Var(X) = \mathbf{E}[(X - \mathbf{E}[X])^2] = p(1-p)^2 + q(0-p)^2 = pq </math>. | The variance is <math>Var(X) = \mathbf{E}[(X - \mathbf{E}[X])^2] = p(1-p)^2 + q(0-p)^2 = pq </math>. | ||
| + | The sum of ''n'' Bernoulli experiments with the same probability of success ''p'' follows a [[Binomial distribution]] ''B(n,p)''. | ||
[[category:Probability and Statistics]] | [[category:Probability and Statistics]] | ||
Revision as of 15:28, July 26, 2011
A Bernoulli experiment (or Bernoulli trial) is the simplest non-trivial random experiment imaginable: it's an experiment of which the outcome is random and can be either of two possibilities: success and failure.
The standard example is tossing a coin.
Expectation and Variance
If the occurrence of a success is encoded as 1 and the occurrence of a failure with 0, then a probability of a success of p (and therefore, of a failure as q=1-p) leads to an expectation of

The variance is 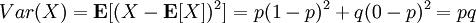 .
.
The sum of n Bernoulli experiments with the same probability of success p follows a Binomial distribution B(n,p).