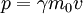Difference between revisions of "Essay:Rebuttal to Counterexamples to Relativity"
(Yikes! That was an unsuccessful test of renumbering. I never meant to save it. Revert.) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| + | 1: ''Despite wasting millions of taxpayer dollars searching for gravity waves predicted by the theory, none has ever been found. Sound like global warming?'' | ||
| + | :This is because the experimental capability to do so doesn't exist. | ||
| − | + | :It has nothing to do with global warming. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | 2: ''The eccentricity of the Moon's orbit is increasing contrary to the theory of relativity'' | ||
| + | :This could be a counterexample to both GR and Newtonian gravity--in both, the eccentricity is defined in terms of conserved quantities. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | : | + | 3: ''Subatomic particles have a speed observed to be faster than the speed of light, which contradicts a fundamental assumption of Relativity.[4] The Italian lab that "shocked the scientific world" has announced more precise results, confirming their previous announcement''. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
:This is an interesting observation. The world's best scientific minds are looking into it. That relativity is incorrect is not being taken seriously as a possible explanation. | :This is an interesting observation. The world's best scientific minds are looking into it. That relativity is incorrect is not being taken seriously as a possible explanation. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4: ''The Pioneer anomaly.'' | ||
:The "Pioneer anomaly" is the deviation in the motion of the Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 spacecraft from their predicted motion, at the distance of Saturn and beyond. It should be noted that the anomaly is about 1000 times greater than the difference between the classical Newtonian prediction and the prediction of relativity, so this is not a problem with relativity ''per se''; it is more general than that. | :The "Pioneer anomaly" is the deviation in the motion of the Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 spacecraft from their predicted motion, at the distance of Saturn and beyond. It should be noted that the anomaly is about 1000 times greater than the difference between the classical Newtonian prediction and the prediction of relativity, so this is not a problem with relativity ''per se''; it is more general than that. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 26: | ||
| − | + | 5: ''Anomalies in the locations of spacecraft that have flown by Earth ("flybys").'' | |
:This may be another case of the Pioneer anomaly, or it may be something else. However, it is very unlikely that it shows that relativity is wrong and Newtonian mechanics is correct. | :This may be another case of the Pioneer anomaly, or it may be something else. However, it is very unlikely that it shows that relativity is wrong and Newtonian mechanics is correct. | ||
| − | + | 6: ''Spiral galaxies confound Relativity, and unseen "dark matter" has been invented to try to retrofit observations to the theory.'' | |
:Correct me if I'm wrong, but wasn't it due to the acceleration of various parts of galaxies that accelerated funny that led to dark matter (based on simple Newtonian dynamics)? | :Correct me if I'm wrong, but wasn't it due to the acceleration of various parts of galaxies that accelerated funny that led to dark matter (based on simple Newtonian dynamics)? | ||
| − | + | 7: ''The acceleration in the expansion of the universe confounds Relativity, and unseen "dark energy" has been invented to try to retrofit observations to the theory.'' | |
:Uh-oh....the dark energy/cosmological constant argument....That term was added by Einstein after he discovered that his field equations (<math>\mathbf{G}=8\pi \mathbf{T}</math>) predicted that the universe was expanding, contradicting his firm philosophical belief in a static universe. So he inserted <math>\Lambda \mathbf{g}</math> to the LHS so that it would predict a static universe. A few years later, Hubble showed the universe to be expanding, and Einstein called the cosmological constant the worst mistake of his career. So, it sort of had a bad reputation, and people didn't want to seriously consider it, until recent observations have shown the universe's expansion to be accelerating forced them to do so. It could have had a very different history. Einstein could have had that term in the EFE's from the start, and pointed out that it would determine if the universe's expansion was accelerating (or not expanding at all!) and it would take further observation to determine its value. | :Uh-oh....the dark energy/cosmological constant argument....That term was added by Einstein after he discovered that his field equations (<math>\mathbf{G}=8\pi \mathbf{T}</math>) predicted that the universe was expanding, contradicting his firm philosophical belief in a static universe. So he inserted <math>\Lambda \mathbf{g}</math> to the LHS so that it would predict a static universe. A few years later, Hubble showed the universe to be expanding, and Einstein called the cosmological constant the worst mistake of his career. So, it sort of had a bad reputation, and people didn't want to seriously consider it, until recent observations have shown the universe's expansion to be accelerating forced them to do so. It could have had a very different history. Einstein could have had that term in the EFE's from the start, and pointed out that it would determine if the universe's expansion was accelerating (or not expanding at all!) and it would take further observation to determine its value. | ||
| − | + | 8: ''Increasingly precise measurements of the advance of the perihelion of Mercury show a shift greater than predicted by Relativity, well beyond the margin of error.'' | |
:A footnote goes on to say that "In a complicated or contrived series of calculations that most physics majors cannot duplicate even after learning them, the theory of general relativity's fundamental formula, <math>G_{\mu\nu} = 8 \pi K T_{\mu\nu}\,</math>, was conformed to match Mercury's then-observed precession of 5600.0 arc-seconds per century. Subsequently, however, more sophisticated technology has measured a different value of this precession (5599.7 arc-seconds per century, with a margin of error of only 0.01) ..." | :A footnote goes on to say that "In a complicated or contrived series of calculations that most physics majors cannot duplicate even after learning them, the theory of general relativity's fundamental formula, <math>G_{\mu\nu} = 8 \pi K T_{\mu\nu}\,</math>, was conformed to match Mercury's then-observed precession of 5600.0 arc-seconds per century. Subsequently, however, more sophisticated technology has measured a different value of this precession (5599.7 arc-seconds per century, with a margin of error of only 0.01) ..." | ||
| Line 60: | Line 58: | ||
| − | + | 9: ''The discontinuity in momentum as velocity approaches "c" for infinitesimal mass, compared to the momentum of light.'' | |
:The formulas for velocity, momentum, and mass can in fact be written in such a way that they appear to have discontinuities, just as the tangent function has discontinuities while the underlying sine and cosine functions do not. But they can also be written in a form that does not show discontinuities. | :The formulas for velocity, momentum, and mass can in fact be written in such a way that they appear to have discontinuities, just as the tangent function has discontinuities while the underlying sine and cosine functions do not. But they can also be written in a form that does not show discontinuities. | ||
:All particles, with or without mass, can have any value of momentum. The formula for the velocity of a particle, in terms of its mass and momentum, is | :All particles, with or without mass, can have any value of momentum. The formula for the velocity of a particle, in terms of its mass and momentum, is | ||
| Line 68: | Line 66: | ||
| − | + | 10: ''The logical problem of a force which is applied at a right angle to the velocity of a relativistic mass - does this act on the rest mass or the relativistic mass?'' | |
:The simple answer is, unequivocally, that it acts on the 'relativistic' mass. The question seems to relate to a simple misunderstanding of Special Relativity. Einstein's theories lead to the conclusion that observers in different inertial frames of reference (i.e. observers with differing, but constant velocities relative to the thing being observed) will observe different inertial masses in the body being observed. However, there is no variance in the body's mass with regard to the direction of the force. Thus to a given observer, a force in any direction will operate on the same mass. However, to a different observer, this mass may be different, although still the constant with regard to the direction of the force. | :The simple answer is, unequivocally, that it acts on the 'relativistic' mass. The question seems to relate to a simple misunderstanding of Special Relativity. Einstein's theories lead to the conclusion that observers in different inertial frames of reference (i.e. observers with differing, but constant velocities relative to the thing being observed) will observe different inertial masses in the body being observed. However, there is no variance in the body's mass with regard to the direction of the force. Thus to a given observer, a force in any direction will operate on the same mass. However, to a different observer, this mass may be different, although still the constant with regard to the direction of the force. | ||
| − | + | 11:''The observed lack of curvature in overall space.'' | |
:What? Is has been observed | :What? Is has been observed | ||
| − | + | 12: ''The universe shortly after its creation, when quantum effects dominated and contradicted Relativity.'' | |
:We're still working on a quantum theory of gravity; this isn't so much a counter-example as saying that (classical)GR isn't valid in that domain. | :We're still working on a quantum theory of gravity; this isn't so much a counter-example as saying that (classical)GR isn't valid in that domain. | ||
| − | + | 13: ''The action-at-a-distance of quantum entanglement.'' | |
:Special Relativity only forbids the transmission of matter, energy or information at a speed faster than light. There are plenty of other things that can move faster than light. Consider a laser on Earth which is rotating on a pivot, whose light shines onto the hull of a satellite 200,000Km away (2e8 metres). If the laser rotates at a sedentary one revolution ever four seconds, the speed of the laser beam's tip crossing the satellite's hull is 3.14e8 metres per second - faster than the speed of light. However, this is not a transfer of information. Any information is travelling from Earth to the satellite, obeying the universal speed limit. Similarly, the only information that can be transmitted by the quantum entanglement of two particles is from the originator of the particles to the two observers, not from one observer to another. Faster than light transmission of information using quantum entanglement has never been observed, nor has even conceived how such a mechanism might work.<ref>http://curious.astro.cornell.edu/question.php?number=612</ref> | :Special Relativity only forbids the transmission of matter, energy or information at a speed faster than light. There are plenty of other things that can move faster than light. Consider a laser on Earth which is rotating on a pivot, whose light shines onto the hull of a satellite 200,000Km away (2e8 metres). If the laser rotates at a sedentary one revolution ever four seconds, the speed of the laser beam's tip crossing the satellite's hull is 3.14e8 metres per second - faster than the speed of light. However, this is not a transfer of information. Any information is travelling from Earth to the satellite, obeying the universal speed limit. Similarly, the only information that can be transmitted by the quantum entanglement of two particles is from the originator of the particles to the two observers, not from one observer to another. Faster than light transmission of information using quantum entanglement has never been observed, nor has even conceived how such a mechanism might work.<ref>http://curious.astro.cornell.edu/question.php?number=612</ref> | ||
| − | + | 14: ''The action-at-a-distance by Jesus, described in John 4:46-54, Matthew 15:28, and Matthew 27:51.'' | |
:As an argument against relativity, there are two reasons that this is invalid (beyond simply questioning the evidential validity of the Bible): | :As an argument against relativity, there are two reasons that this is invalid (beyond simply questioning the evidential validity of the Bible): | ||
::a) These passages clearly refer to a [[miracle]]. A miracle, being an act of God, is not subject to the laws of physics. | ::a) These passages clearly refer to a [[miracle]]. A miracle, being an act of God, is not subject to the laws of physics. | ||
| Line 93: | Line 91: | ||
:::ii) It must be considered that at the time when the Gospels were written, neither their authors nor their intended readers were aware of any concept of the speed of light and were unable to measure the billionths of a second difference between the events being considered here. Thus just as in modern parlance the phrase 'at the same moment' has a tolerance of milliseconds (unless specifically couched to mean otherwise) so do the various terms used by the Evangelists. They would never have considered it an important issue, and would therefore not have worried about the degree of precision. | :::ii) It must be considered that at the time when the Gospels were written, neither their authors nor their intended readers were aware of any concept of the speed of light and were unable to measure the billionths of a second difference between the events being considered here. Thus just as in modern parlance the phrase 'at the same moment' has a tolerance of milliseconds (unless specifically couched to mean otherwise) so do the various terms used by the Evangelists. They would never have considered it an important issue, and would therefore not have worried about the degree of precision. | ||
| − | + | 15: ''The failure to discover gravitons, despite wasting hundreds of millions in taxpayer money in searching.'' | |
: Gravitons are a prediction of [[Quantum Theory]], not of relativity, although the concept is an extension of the relativistic idea that forces take a finite time to be transmitted over a distance. However, as with the failure to detect gravity waves (see 1 above), the lack of detection is conformant with the expectation that they would be unlikely to be detected with current technology. | : Gravitons are a prediction of [[Quantum Theory]], not of relativity, although the concept is an extension of the relativistic idea that forces take a finite time to be transmitted over a distance. However, as with the failure to detect gravity waves (see 1 above), the lack of detection is conformant with the expectation that they would be unlikely to be detected with current technology. | ||
| − | + | 16: ''Newly observed data reveal that the fine-structure constant, α (alpha), actually varies throughout the universe, demonstrating that all inertial frames of reference do not experience identical laws of physics as claimed by Relativity'' | |
: Whilst this observation is unconfirmed, if true it would still not invalidate relativity. Many things may vary with position in space, and relativity does not deny this. There is no suggestion that the fine-structure constant is different at the same point in space for observers in different non-inertial frame, as the 'counterexample' implies. | : Whilst this observation is unconfirmed, if true it would still not invalidate relativity. Many things may vary with position in space, and relativity does not deny this. There is no suggestion that the fine-structure constant is different at the same point in space for observers in different non-inertial frame, as the 'counterexample' implies. | ||
| − | + | 17: | |
| − | + | 18: ''The change in mass over time of standard kilograms preserved under ideal conditions.'' | |
:Clearly there are a few dots that need to be joined here before this can become a coherent argument for or against anything. The best interpretation that can be put on it is that the [[Law of the conservation of mass|principle of conservation]] of mass is being violated. However relativity, with its concept of mass/energy equivalence, holds to a more general [[Principle of conservation of energy|principle of conservation of energy]]. Thus relativity might easily explain the observation, as keeping the standard masses in a perfect energy isolated environment is a far harder task than keeping them in a matter isolated environment (which is itself not perfectly achievable). | :Clearly there are a few dots that need to be joined here before this can become a coherent argument for or against anything. The best interpretation that can be put on it is that the [[Law of the conservation of mass|principle of conservation]] of mass is being violated. However relativity, with its concept of mass/energy equivalence, holds to a more general [[Principle of conservation of energy|principle of conservation of energy]]. Thus relativity might easily explain the observation, as keeping the standard masses in a perfect energy isolated environment is a far harder task than keeping them in a matter isolated environment (which is itself not perfectly achievable). | ||
:However, until specific explanations for the variations in mass of the various standard bodies are offered, there is no foundation to any speculation as to what laws of physics are involved, let alone whether they are being violated. | :However, until specific explanations for the variations in mass of the various standard bodies are offered, there is no foundation to any speculation as to what laws of physics are involved, let alone whether they are being violated. | ||
| − | + | 19: | |
| − | + | 20: | |
| − | + | 21: | |
| − | + | 22: | |
| − | + | 23: | |
| − | + | 24: | |
| − | + | 25: | |
| − | + | 26: ''Relativity requires that anything traveling at the speed of light must have mass zero, so it must have momentum zero. But the laws of electrodynamics require that light have nonzero momentum.'' | |
:This seems to be another basic misunderstanding of relativity, from someone who gave up halfway through the textbook. Newtonian momentum (p = mv) does certainly indicate that a body with zero mass (''m'') must have zero momentum whatever its velocity (''v''). However, the relativistic equation for momentum is: | :This seems to be another basic misunderstanding of relativity, from someone who gave up halfway through the textbook. Newtonian momentum (p = mv) does certainly indicate that a body with zero mass (''m'') must have zero momentum whatever its velocity (''v''). However, the relativistic equation for momentum is: | ||
| Line 144: | Line 142: | ||
| − | + | 27: ''Relativity requires different values for the inertia of a moving object: in its direction of motion, and perpendicular to that direction. This contradicts the logical principle that the laws of physics are the same in all directions.'' | |
:The rules for calculating inertia and other questions of mechanics are well known. The inertia, that is, the way that a force affects an object's momentum, is well known. Hundreds of physics textbooks discuss this in great detail, in terms of the Lorentz transform and the concepts of the force and momentum 4-vectors. The "inertia" comes from what is now called the mass, which used to be called the "rest mass". Archaic treatments formulated this in terms of the "relativistic mass", which was different. The mass is a scalar, and has no direction. The formulas for calculating the motion in terms of forces, in the direction of motion or transverse to it, are well known. | :The rules for calculating inertia and other questions of mechanics are well known. The inertia, that is, the way that a force affects an object's momentum, is well known. Hundreds of physics textbooks discuss this in great detail, in terms of the Lorentz transform and the concepts of the force and momentum 4-vectors. The "inertia" comes from what is now called the mass, which used to be called the "rest mass". Archaic treatments formulated this in terms of the "relativistic mass", which was different. The mass is a scalar, and has no direction. The formulas for calculating the motion in terms of forces, in the direction of motion or transverse to it, are well known. | ||
| − | + | 28: | |
| − | + | 29: | |
| − | + | 30: | |
| − | + | 31: ''The Twin Paradox'' | |
:The physics and mathematics underlying the "twin paradox" are well known. That one of the twins will have had to undergo different accelerations from the other before returning to the same point is what enables them to perceive different passage of time. This does not contradict relativity, and Einstein never said that it does. His explanation in terms of different acceleration is correct. | :The physics and mathematics underlying the "twin paradox" are well known. That one of the twins will have had to undergo different accelerations from the other before returning to the same point is what enables them to perceive different passage of time. This does not contradict relativity, and Einstein never said that it does. His explanation in terms of different acceleration is correct. | ||
| Line 161: | Line 159: | ||
| − | + | 32: | |
| − | + | 33: ''Based on Relativity, Einstein claimed in 1909 that the aether does not exist, but in order to make subatomic physics work right, theorists had to introduce the aether-like concept of the Higgs field, which fills all of space and breaks symmetries.'' | |
:Quantum field theory abounds with fields. The Higgs particle has a Higgs field. It has nothing to do with the "luminiferous aether". | :Quantum field theory abounds with fields. The Higgs particle has a Higgs field. It has nothing to do with the "luminiferous aether". | ||
| − | + | 34: | |
| − | + | 35: ''Minkowski space is predicated on the idea of four-dimensional vectors of which one component is time. However, one of the properties of a vector space is that every vector have an inverse. Time cannot be a vector because it has no inverse.'' | |
:Time isn't a vector. It is a component of the vector space known as "spacetime". Vectors have negatives; the word "inverse" is not typically used here. While there are thermodynamic and other reasons for not allowing time to go backwards in the real world, the mathematics of spacetime allow vectors with any components, even negative ones. | :Time isn't a vector. It is a component of the vector space known as "spacetime". Vectors have negatives; the word "inverse" is not typically used here. While there are thermodynamic and other reasons for not allowing time to go backwards in the real world, the mathematics of spacetime allow vectors with any components, even negative ones. | ||
| − | + | 36: | |
| − | + | 37: | |
| − | + | 38: ''Experiments in electromagnetic induction contradict Relativity: "Einstein's Relativity ... can not explain the experiment in graph 2, in which moving magnetic field has not produced electric field."'' | |
:The first cited reference, from which the quote was taken, is a totally crackpot web page, from a web site that seems to specialize in hosting crackpot papers. The writing is essentially illiterate and incoherent, as in this sentence: "According to Faraday's Law it can be explained as that, duo to the magnetic flux in conductor line changing, firstly induced electromotive force dU coming from the line-winded conductor to bring out voltage, then based on differential form <math>I = \frac{-\sigma s dU}{dl}</math> of Ohm's Law, the physical natural would be regarded as 'voltage before electric current' " | :The first cited reference, from which the quote was taken, is a totally crackpot web page, from a web site that seems to specialize in hosting crackpot papers. The writing is essentially illiterate and incoherent, as in this sentence: "According to Faraday's Law it can be explained as that, duo to the magnetic flux in conductor line changing, firstly induced electromotive force dU coming from the line-winded conductor to bring out voltage, then based on differential form <math>I = \frac{-\sigma s dU}{dl}</math> of Ohm's Law, the physical natural would be regarded as 'voltage before electric current' " | ||
| − | + | 39: ''Relativity breaks down if a solenoid is traveling at or near the speed of light.'' | |
:The equations of electrodynamics (Maxwell's equations), and their connection with relativity, are well known. Hundreds of electrodynamics textbooks cover this subject. The equations are correct at all realizable speeds, even relativistic (''near'' the speed of light) speeds. (Maxwell's equations are said to be the only equations from classical physics that did not need to be modified for relativity.) The equations correctly describe the behavior of magnets (this is presumably what was meant by "solenoids"), charges, and electric and magnetic fields, even at speeds near the speed of light. Of course the equations don't work ''at'' the speed of light. The cited article never discussed speeds ''near'' the speed of light, only ''at'' the speed of light. The questioner was rightly taken to task for his physically unrealizable assumption. | :The equations of electrodynamics (Maxwell's equations), and their connection with relativity, are well known. Hundreds of electrodynamics textbooks cover this subject. The equations are correct at all realizable speeds, even relativistic (''near'' the speed of light) speeds. (Maxwell's equations are said to be the only equations from classical physics that did not need to be modified for relativity.) The equations correctly describe the behavior of magnets (this is presumably what was meant by "solenoids"), charges, and electric and magnetic fields, even at speeds near the speed of light. Of course the equations don't work ''at'' the speed of light. The cited article never discussed speeds ''near'' the speed of light, only ''at'' the speed of light. The questioner was rightly taken to task for his physically unrealizable assumption. | ||
Revision as of 04:39, February 1, 2012
This is intended as an article rebutting the points in the Counterexamples to Relativity article. That article's talk page has proven to be less than satisfactory for this purpose, because it gets archived, and much of its material has degenerated into personal disputes. We believe that the two sides of the issue are better handled in two articles—this one and Counterexamples to Relativity, rather than a talk page.
Unlike most essay pages, anyone is welcome to contribute. We ask that you abide by the usual guidelines—do not remove non-vandal, non-parody, non-libelous material without discussing it first on the talk page, or explaining after-the-fact for serious problems.
1: Despite wasting millions of taxpayer dollars searching for gravity waves predicted by the theory, none has ever been found. Sound like global warming?
- This is because the experimental capability to do so doesn't exist.
- It has nothing to do with global warming.
2: The eccentricity of the Moon's orbit is increasing contrary to the theory of relativity
- This could be a counterexample to both GR and Newtonian gravity--in both, the eccentricity is defined in terms of conserved quantities.
3: Subatomic particles have a speed observed to be faster than the speed of light, which contradicts a fundamental assumption of Relativity.[4] The Italian lab that "shocked the scientific world" has announced more precise results, confirming their previous announcement.
- This is an interesting observation. The world's best scientific minds are looking into it. That relativity is incorrect is not being taken seriously as a possible explanation.
4: The Pioneer anomaly.
- The "Pioneer anomaly" is the deviation in the motion of the Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 spacecraft from their predicted motion, at the distance of Saturn and beyond. It should be noted that the anomaly is about 1000 times greater than the difference between the classical Newtonian prediction and the prediction of relativity, so this is not a problem with relativity per se; it is more general than that.
- Calculating the force caused by heat (that is, miniscule amounts of infrared radiation) from the radioactive power source was one of the first effects that was examined. The anomaly arose when this and other known effects could not fully explain the deviation.
- The problem is believed to have been solved by taking into account the reflection of the radiation from the power source off of the back of the antenna dish[1]. The solution is sometimes described as an application of "Phong shading", a technique of computer graphics that is now considered imprecise. But Phong shading itself is not what is important. The "ray tracing" computer graphics technique that underlies Phong shading was what inspired the scientists to take reflection into account.
5: Anomalies in the locations of spacecraft that have flown by Earth ("flybys").
- This may be another case of the Pioneer anomaly, or it may be something else. However, it is very unlikely that it shows that relativity is wrong and Newtonian mechanics is correct.
6: Spiral galaxies confound Relativity, and unseen "dark matter" has been invented to try to retrofit observations to the theory.
- Correct me if I'm wrong, but wasn't it due to the acceleration of various parts of galaxies that accelerated funny that led to dark matter (based on simple Newtonian dynamics)?
7: The acceleration in the expansion of the universe confounds Relativity, and unseen "dark energy" has been invented to try to retrofit observations to the theory.
- Uh-oh....the dark energy/cosmological constant argument....That term was added by Einstein after he discovered that his field equations (
 ) predicted that the universe was expanding, contradicting his firm philosophical belief in a static universe. So he inserted
) predicted that the universe was expanding, contradicting his firm philosophical belief in a static universe. So he inserted  to the LHS so that it would predict a static universe. A few years later, Hubble showed the universe to be expanding, and Einstein called the cosmological constant the worst mistake of his career. So, it sort of had a bad reputation, and people didn't want to seriously consider it, until recent observations have shown the universe's expansion to be accelerating forced them to do so. It could have had a very different history. Einstein could have had that term in the EFE's from the start, and pointed out that it would determine if the universe's expansion was accelerating (or not expanding at all!) and it would take further observation to determine its value.
to the LHS so that it would predict a static universe. A few years later, Hubble showed the universe to be expanding, and Einstein called the cosmological constant the worst mistake of his career. So, it sort of had a bad reputation, and people didn't want to seriously consider it, until recent observations have shown the universe's expansion to be accelerating forced them to do so. It could have had a very different history. Einstein could have had that term in the EFE's from the start, and pointed out that it would determine if the universe's expansion was accelerating (or not expanding at all!) and it would take further observation to determine its value.
8: Increasingly precise measurements of the advance of the perihelion of Mercury show a shift greater than predicted by Relativity, well beyond the margin of error.
- A footnote goes on to say that "In a complicated or contrived series of calculations that most physics majors cannot duplicate even after learning them, the theory of general relativity's fundamental formula,
 , was conformed to match Mercury's then-observed precession of 5600.0 arc-seconds per century. Subsequently, however, more sophisticated technology has measured a different value of this precession (5599.7 arc-seconds per century, with a margin of error of only 0.01) ..."
, was conformed to match Mercury's then-observed precession of 5600.0 arc-seconds per century. Subsequently, however, more sophisticated technology has measured a different value of this precession (5599.7 arc-seconds per century, with a margin of error of only 0.01) ..."
- Considering only the anomalous precession, that is, the precession that remains after all known other factors (other planets and asteroids, solar oblateness) have been accounted for, general relativity predicts 42.98 ±0.04 arcseconds per century. Some observed values are:
- 43.11 ± 0.21 (Shapiro et al., 1976)
- 42.92 ± 0.20 (Anderson et al., 1987)
- 42.94 ± 0.20 (Anderson et al., 1991)
- 43.13 ± 0.14 (Anderson et al., 1992)
- [Source: Pijper 2008]
- These error bars, and that of the relativity formula, all overlap.
- The formula for mechanics under general relativity is complicated, but it is not contrived or conformed. "Conformed" suggests that it was somehow adjusted or "tweaked" to match the 42.98 figure. The formula is
- To begin to explain the formula, Newton's law of gravity, combining F = ma and
 , is
, is
- In Einstein's equation,
 is the "stress-energy tensor", and
is the "stress-energy tensor", and  gives the density of the Sun, taking the place of
gives the density of the Sun, taking the place of  .
.  is the "Einstein curvature tensor", and says how spacetime curves to create an apparent gravitational acceleration.
is the "Einstein curvature tensor", and says how spacetime curves to create an apparent gravitational acceleration. - There is nothing to tweak to get a value of 42.98 arcseconds. 8 is 8.
 is
is  . K is Newton's constant of gravitation in both formulas.
. K is Newton's constant of gravitation in both formulas.
9: The discontinuity in momentum as velocity approaches "c" for infinitesimal mass, compared to the momentum of light.
- The formulas for velocity, momentum, and mass can in fact be written in such a way that they appear to have discontinuities, just as the tangent function has discontinuities while the underlying sine and cosine functions do not. But they can also be written in a form that does not show discontinuities.
- All particles, with or without mass, can have any value of momentum. The formula for the velocity of a particle, in terms of its mass and momentum, is
- For a particle with mass, this means that momentum of zero gives a speed of zero, and, as the momentum approaches infinity, the speed approaches c.
- For a massless particle, the speed is always c.
10: The logical problem of a force which is applied at a right angle to the velocity of a relativistic mass - does this act on the rest mass or the relativistic mass?
- The simple answer is, unequivocally, that it acts on the 'relativistic' mass. The question seems to relate to a simple misunderstanding of Special Relativity. Einstein's theories lead to the conclusion that observers in different inertial frames of reference (i.e. observers with differing, but constant velocities relative to the thing being observed) will observe different inertial masses in the body being observed. However, there is no variance in the body's mass with regard to the direction of the force. Thus to a given observer, a force in any direction will operate on the same mass. However, to a different observer, this mass may be different, although still the constant with regard to the direction of the force.
11:The observed lack of curvature in overall space.
- What? Is has been observed
12: The universe shortly after its creation, when quantum effects dominated and contradicted Relativity.
- We're still working on a quantum theory of gravity; this isn't so much a counter-example as saying that (classical)GR isn't valid in that domain.
13: The action-at-a-distance of quantum entanglement.
- Special Relativity only forbids the transmission of matter, energy or information at a speed faster than light. There are plenty of other things that can move faster than light. Consider a laser on Earth which is rotating on a pivot, whose light shines onto the hull of a satellite 200,000Km away (2e8 metres). If the laser rotates at a sedentary one revolution ever four seconds, the speed of the laser beam's tip crossing the satellite's hull is 3.14e8 metres per second - faster than the speed of light. However, this is not a transfer of information. Any information is travelling from Earth to the satellite, obeying the universal speed limit. Similarly, the only information that can be transmitted by the quantum entanglement of two particles is from the originator of the particles to the two observers, not from one observer to another. Faster than light transmission of information using quantum entanglement has never been observed, nor has even conceived how such a mechanism might work.[2]
14: The action-at-a-distance by Jesus, described in John 4:46-54, Matthew 15:28, and Matthew 27:51.
- As an argument against relativity, there are two reasons that this is invalid (beyond simply questioning the evidential validity of the Bible):
- a) These passages clearly refer to a miracle. A miracle, being an act of God, is not subject to the laws of physics.
- b) It is highly debatable as to whether the verses do describe action-at-a-distance in the sense of an action whose influence travels instantaneously (and therefore faster than the speed of light). This itself may be argued from two viewpoints:
- i) When reading these passages, as with consideration of many apparent relativistic anomalies, the true picture of causality must be considered. In each case there are two apparent events. Event A - Jesus does something (says 'thy son liveth', says 'be it unto thee even as thou wilt', or Christ's spirit leaving His body). Event B - the apparent result (the son lives, her daughter is made whole, or the earth quakes). However, it is not the case in any of these examples that A causes B. Both A and B are caused by a third event. In the first two cases it is Christ's thought that causes the miracle and that causes His lips to announce the miracle. This thought would have occurred fractions of a second before either event, and is the non-instantaneous cause of both. In the last case it is Christ's death that is the precursor and cause of both events.
- b) It is highly debatable as to whether the verses do describe action-at-a-distance in the sense of an action whose influence travels instantaneously (and therefore faster than the speed of light). This itself may be argued from two viewpoints:
- ii) It must be considered that at the time when the Gospels were written, neither their authors nor their intended readers were aware of any concept of the speed of light and were unable to measure the billionths of a second difference between the events being considered here. Thus just as in modern parlance the phrase 'at the same moment' has a tolerance of milliseconds (unless specifically couched to mean otherwise) so do the various terms used by the Evangelists. They would never have considered it an important issue, and would therefore not have worried about the degree of precision.
15: The failure to discover gravitons, despite wasting hundreds of millions in taxpayer money in searching.
- Gravitons are a prediction of Quantum Theory, not of relativity, although the concept is an extension of the relativistic idea that forces take a finite time to be transmitted over a distance. However, as with the failure to detect gravity waves (see 1 above), the lack of detection is conformant with the expectation that they would be unlikely to be detected with current technology.
16: Newly observed data reveal that the fine-structure constant, α (alpha), actually varies throughout the universe, demonstrating that all inertial frames of reference do not experience identical laws of physics as claimed by Relativity
- Whilst this observation is unconfirmed, if true it would still not invalidate relativity. Many things may vary with position in space, and relativity does not deny this. There is no suggestion that the fine-structure constant is different at the same point in space for observers in different non-inertial frame, as the 'counterexample' implies.
17:
18: The change in mass over time of standard kilograms preserved under ideal conditions.
- Clearly there are a few dots that need to be joined here before this can become a coherent argument for or against anything. The best interpretation that can be put on it is that the principle of conservation of mass is being violated. However relativity, with its concept of mass/energy equivalence, holds to a more general principle of conservation of energy. Thus relativity might easily explain the observation, as keeping the standard masses in a perfect energy isolated environment is a far harder task than keeping them in a matter isolated environment (which is itself not perfectly achievable).
- However, until specific explanations for the variations in mass of the various standard bodies are offered, there is no foundation to any speculation as to what laws of physics are involved, let alone whether they are being violated.
19:
20:
21:
22:
23:
24:
25:
26: Relativity requires that anything traveling at the speed of light must have mass zero, so it must have momentum zero. But the laws of electrodynamics require that light have nonzero momentum.
- This seems to be another basic misunderstanding of relativity, from someone who gave up halfway through the textbook. Newtonian momentum (p = mv) does certainly indicate that a body with zero mass (m) must have zero momentum whatever its velocity (v). However, the relativistic equation for momentum is:
- where m0 is the rest mass of the object and γ is the Lorentz factor, given by
- where c is the speed of light.
- For the case of a photon, where rest mass is zero and v is equal to c, this gives p as zero divided by zero - an undetermined value.
- However, with the substitution of the famous E=mc2, where E is the energy of the body, the momentum equation can be rearranged to:
- With a photon of zero rest mass, this gives:
- Finally, substituting Planck's Equation for the energy of a photon
 where h is Planck's Constant and f is the frequency of the photon, we get the familiar (and experimentally demonstrated) value for a photon's momentum of:
where h is Planck's Constant and f is the frequency of the photon, we get the familiar (and experimentally demonstrated) value for a photon's momentum of:
- where
 is the photon's wavelength.[3]
is the photon's wavelength.[3]
27: Relativity requires different values for the inertia of a moving object: in its direction of motion, and perpendicular to that direction. This contradicts the logical principle that the laws of physics are the same in all directions.
- The rules for calculating inertia and other questions of mechanics are well known. The inertia, that is, the way that a force affects an object's momentum, is well known. Hundreds of physics textbooks discuss this in great detail, in terms of the Lorentz transform and the concepts of the force and momentum 4-vectors. The "inertia" comes from what is now called the mass, which used to be called the "rest mass". Archaic treatments formulated this in terms of the "relativistic mass", which was different. The mass is a scalar, and has no direction. The formulas for calculating the motion in terms of forces, in the direction of motion or transverse to it, are well known.
28:
29:
30:
31: The Twin Paradox
- The physics and mathematics underlying the "twin paradox" are well known. That one of the twins will have had to undergo different accelerations from the other before returning to the same point is what enables them to perceive different passage of time. This does not contradict relativity, and Einstein never said that it does. His explanation in terms of different acceleration is correct.
- The comment about extending the length of the trip so that the acceleration would be de minimis is wrong. It seems to suggest that the acceleration could be reduced until it is negligible. It can be reduced by lengthening the trip, but it is not negligible. The Lorentz transform, and the equations of motion, are mathematically exact. The integral of a very small function over a long period is still significant. If the twins followed different paths in spacetime, which they must in order to measure different elapsed proper time, they must have undergone different accelerations, however small those differences may have been.
- Of course, if they never come back to the same point, they could both undergo zero acceleration.
32:
33: Based on Relativity, Einstein claimed in 1909 that the aether does not exist, but in order to make subatomic physics work right, theorists had to introduce the aether-like concept of the Higgs field, which fills all of space and breaks symmetries.
- Quantum field theory abounds with fields. The Higgs particle has a Higgs field. It has nothing to do with the "luminiferous aether".
34:
35: Minkowski space is predicated on the idea of four-dimensional vectors of which one component is time. However, one of the properties of a vector space is that every vector have an inverse. Time cannot be a vector because it has no inverse.
- Time isn't a vector. It is a component of the vector space known as "spacetime". Vectors have negatives; the word "inverse" is not typically used here. While there are thermodynamic and other reasons for not allowing time to go backwards in the real world, the mathematics of spacetime allow vectors with any components, even negative ones.
36:
37:
38: Experiments in electromagnetic induction contradict Relativity: "Einstein's Relativity ... can not explain the experiment in graph 2, in which moving magnetic field has not produced electric field."
- The first cited reference, from which the quote was taken, is a totally crackpot web page, from a web site that seems to specialize in hosting crackpot papers. The writing is essentially illiterate and incoherent, as in this sentence: "According to Faraday's Law it can be explained as that, duo to the magnetic flux in conductor line changing, firstly induced electromotive force dU coming from the line-winded conductor to bring out voltage, then based on differential form
 of Ohm's Law, the physical natural would be regarded as 'voltage before electric current' "
of Ohm's Law, the physical natural would be regarded as 'voltage before electric current' "
39: Relativity breaks down if a solenoid is traveling at or near the speed of light.
- The equations of electrodynamics (Maxwell's equations), and their connection with relativity, are well known. Hundreds of electrodynamics textbooks cover this subject. The equations are correct at all realizable speeds, even relativistic (near the speed of light) speeds. (Maxwell's equations are said to be the only equations from classical physics that did not need to be modified for relativity.) The equations correctly describe the behavior of magnets (this is presumably what was meant by "solenoids"), charges, and electric and magnetic fields, even at speeds near the speed of light. Of course the equations don't work at the speed of light. The cited article never discussed speeds near the speed of light, only at the speed of light. The questioner was rightly taken to task for his physically unrealizable assumption.