Difference between revisions of "Multiplication"
From Conservapedia
m (links) |
m (Recat) |
||
| (37 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | In its most elementary form '''multiplication''' | + | In its most elementary form '''multiplication''' is the repeated [[addition]] of [[whole numbers]] or [[integers]]. |
| − | :For example, <big><math> | + | :For example, <big><math>3\times 2 = 2 + 2 + 2 = 6</math></big> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The result of a multiplication is the ''product''. The numbers which are multiplied together are called ''factors''. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | In this context, it is also one of the most well-known [[commutative]] operations: It yields the same result, regardless of placement of numbers. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | :For example <big><math>3\times 2 = 2\times 3</math></big>. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Multiplication also possesses the [[associative property of multiplication|associative property]]. | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | The opposite of multiplication is [[division]]. | |
| + | |||
| + | == Properties of Multiplication == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Multiplying any number by 1 yields that same number again. E.g. <math>8\times 1 = 1</math> | ||
| + | * Multiplying any number by 0 yields 0. E.g. <math>7\times 0 = 0</math> | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 21: | ||
*[[Arithmetic]] | *[[Arithmetic]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Arithmetic]] |
Latest revision as of 13:37, March 26, 2017
In its most elementary form multiplication is the repeated addition of whole numbers or integers.
- For example,
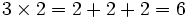
The result of a multiplication is the product. The numbers which are multiplied together are called factors.
In this context, it is also one of the most well-known commutative operations: It yields the same result, regardless of placement of numbers.
- For example
 .
.
Multiplication also possesses the associative property.
The opposite of multiplication is division.
Properties of Multiplication
- Multiplying any number by 1 yields that same number again. E.g.

- Multiplying any number by 0 yields 0. E.g.
