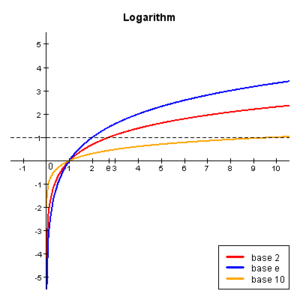
Natural logarithm
From Conservapedia
The natural logarithm,  is the inverse of the function
is the inverse of the function  . In other words, if
. In other words, if  , we define
, we define  .
.
The natural logarithm has some interesting properties that follow from the multiplicative properties of  . The natural logarithm is also particularly useful in calculating interest.
. The natural logarithm is also particularly useful in calculating interest.
Properties of the Logarithm
 for all positive reals
for all positive reals  .
.
Proof: If  , we can write
, we can write  and
and 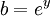 . It follows that
. It follows that  . By definition,
. By definition,  . This last expression, of course, is
. This last expression, of course, is  .
.
Proof: If  is a positive integer, this just follows from repeated application of the above-mentioned additive property of the logarithm. For
is a positive integer, this just follows from repeated application of the above-mentioned additive property of the logarithm. For  , note that the statement follows by observing that
, note that the statement follows by observing that  . Thus,
. Thus,  for all rational numbers
for all rational numbers  . The statement must therefore hold for all reals
. The statement must therefore hold for all reals  by continuity.
by continuity.
Proof:  , hence we must have
, hence we must have  .
.