Difference between revisions of "Cosmological constant"
(This is so bad it's not even wrong. Please see talk page.) |
DavidB4-bot (Talk | contribs) m (→Revival of the cosmological constant vs. property of the correct metric: HTTP --> HTTPS #3, replaced: http://arxiv.org → https://arxiv.org) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Cosmological constant''' is constant <math>\Lambda</math> of Einstein field equation | + | The '''Cosmological constant''' is the constant <math>\Lambda</math> of the Einstein field equation |
| − | :<math>R_{\mu\nu}-(R/2)g_{\mu\nu}+\Lambda g_{\mu\nu}=8\pi T_{\mu\nu}</math>, | + | :<math>R_{\mu\nu}-(R/2)g_{\mu\nu}+\Lambda g_{\mu\nu}=8\pi G T_{\mu\nu}</math>, |
| − | where <math>R_{\mu\nu}</math> is Ricci tensor, <math>R</math> is its contraction, <math>g_{\mu\nu}</math> is metric tensor of spacetime, and <math>T_{\mu\nu}</math> is stress-energy tensor. | + | where <math>R_{\mu\nu}</math> is Ricci's tensor, <math>R</math> is its contraction, <math>g_{\mu\nu}</math> is the metric tensor of spacetime, <math>G</math> is Newton's constant of gravitation, and <math>T_{\mu\nu}</math> is the stress-energy tensor. (The experimentally derived constant <math>G</math> has to appear in both Newton's formulation of gravity and the [[General relativity]] formulation, since they are compatible.) |
| − | Einstein | + | Einstein added the cosmological constant term to his gravitational field equations in order to allow the existence of a homogeneous static solutions in the presence of matter, i.e. to make the universe stationary (neither expanding nor contracting). This works when the cosmological constant has the so-called Einstein value: |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
:<math>\Lambda_E=4\pi G \rho/c^2</math>, | :<math>\Lambda_E=4\pi G \rho/c^2</math>, | ||
| − | where <math> | + | where <math>\rho</math> is the mass density of space and <math>c</math> is the speed of light in vacuo. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Historical background== | ||
| + | [[Image:600px-Albert Einstein Head.jpg|thumbnail|right|200px| | ||
| + | *"I do not share the crusading spirit of the professional [[Atheism|atheist]] whose fervor is mostly due to a painful act of liberation from the fetters of religious indoctrination received in youth. I prefer an attitude of humility corresponding to the weakness of our intellectual understanding of nature and of our own being." - [[Albert Einstein]]<ref name="Isaacson390">Isaacson, Walter (2008). [https://books.google.com/books?id=cdxWNE7NY6QC&pg=PT390 ''Einstein: His Life and Universe''] (New York: Simon and Schuster), p. 390. Retrieved from GoogleBooks archive on February 19, 2015.</ref>]] | ||
| + | In 1915 Einstein introduced the field equation that placed into balance and found equal the [[Curvature of space|curvature]] at one side and [[Mass (science)|mass]] on the other. He hoped that the equations of [[general relativity]] would determine a single universe model without any beginning or end. For reasons he could never make clear, he found universe so conceived particularly satisfying and he managed to find a solution to his own equations that specified universe of that sort, static and unchanged forever.<ref name="Devils"/>{{#tag:ref|The contemporary atheistic scientists such as [[Stephen Hawking|S.Hawking]] believe there is no room for creator in the universe which has no boundary or edge whereas in universe which had beginning we could suppose it had a creator.<ref name="WhomadeGod">{{cite book | ||
| + | |author=Edgar Anrews | ||
| + | |title= Who made God? Searching for a theory of everything. | ||
| + | |publisher= EP Books | ||
| + | |location= Carlisle, PA, USA | ||
| + | |year= 2010 | ||
| + | |pages=98, 100 | ||
| + | |isbn=978-0-85234-707-2 | ||
| + | |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EOFfAAAACAAJ&dq=Andrews+who+made+God&source=bl&ots=5Ru2cf9HRQ&sig=PilSMEqTMAmqtoUgJ9idnBQpH64&hl=en&sa=X&ei=099xUNuqE43KtAa8uICIDA&redir_esc=y | ||
| + | |quote= Stephen Hawking puts it thus: 'So long as the universe had a beginning, we could suppose it had a creator. But if universe is really completely self-contained, having no boundary or edge, it would have neither beginning not end; it would simply be. What place then for creator?'}}</ref> See also: [[Singularity#Antipathy to the idea of beginning|Antipathy to the idea of beginning]]|group=note}} A.G. Riess declares that Einstein's original idea was to have constant amount of energy in the space.<ref name="RiessNobel"/> When in 1920s Russian mathematician A.Friedman (1924)<ref name="Friedman">{{cite web | ||
| + | |author=Alexander Friedmann | ||
| + | |title=Über die Möglichkeit einer Welt mit konstanter negativer Krümmung des Raumes | ||
| + | |publisher=Zeitschrift für Physik | ||
| + | |volume=21 | ||
| + | |issue=1 | ||
| + | |pages=326–332 | ||
| + | |url=http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1924ZPhy...21..326F | ||
| + | |doi=10.1007/BF01328280 | ||
| + | |language=German}}</ref> and Belgian catholic priest and professor of physics G.Lemaître (1927)<ref>{{Cite web|author=G. Lemaître |title=Un Univers homogène de masse constante et de rayon croissant rendant compte de la vitesse radiale des nébuleuses extra-galactiques |journal=Annales de la Société Scientifique de Bruxelles |volume=47 |page=49 |month=April |year=1927 |url=http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-iarticle_query?1927ASSB...47...49L&defaultprint=YES&filetype=.pdf |language=French}}</ref> independently found that Einstein's gravitational field equations of [[general relativity]] have non-static cosmological solution<ref name="Devils">{{Cite book | ||
| + | | author = David Berlinski | ||
| + | | title = The Devil’s Delusion | ||
| + | | publisher = Basic Books, New York, 2009 | ||
| + | | isbn = 978-0-465-01937-3 | ||
| + | | pages = 77 | ||
| + | |chapter = The Cause | ||
| + | | url=http://www.davidberlinski.org/devils-delusion/about.php | ||
| + | | quote = }}</ref> implying an [[Expanding universe|expanding]] or collapsing universe,<ref name="DismantlingBB">{{cite book|author=Alex Williams, John Hartnett|title=Dismantling the Big Bang|publisher=Master Books|location=Green Forest, AR, USA|year=2005|pages=110|isbn=978-0-89051-437-5|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EvN9Gfbox74C&printsec=frontcover&dq=Dismantling+Big&source=bl&ots=uuIXDOw4ld&sig=wWFH6PJy2ZW5JQc8N59jTX5FVd0&hl=en&sa=X&ei=9WlsUJ-cJ8bGtAasp4H4Bg&redir_esc=y#v=snippet&q=CSR&f=false|quote=...his equations were telling [Einstein] that [the universe] had to be either collapsing or expanding...A large value [of cosmological constant] would cause large redshifts and spacial distortion in nearby objects...[the cosmological constant ...involves fine-tuning of over 120 orders of magnitude (quoted Lawrence Krauss)]}}</ref> Einstein, wishing to cancel out expansion, suggested modification to his field equations by adding a so-called cosmological term.<ref name="CSR">{{cite book | ||
| + | |author=Moshe Carmeli | ||
| + | |title=Cosmological Special Relativity, The Large-Scale Structure of Space, Time and Velocity, 2nd Edition | ||
| + | |publisher=World Scientific Publishing | ||
| + | |year=2002 | ||
| + | |pages=2, 168 | ||
| + | |url=http://www.creationbookpublishers.com/products/Without-Excuse.html | ||
| + | |isbn=9-789-02-4936-5 | ||
| + | |quote= | ||
| + | }}</ref> {{#tag:ref|cf."the 'cosmological constant' ... [also] had the effect of balancing the gravitational attraction that would otherwise cause the universe to collapse"<ref name="WhomadeGod"/>|group=note}} Before long, after [[Edwin Hubble|Hubble]]'s interpretation of new [[Scientific discovery|discoveries]] as [[expanding universe]] in 1929, the role of cosmological constant aiming to allow static homogeneous solutions to field equations in presence of [[matter]] seemed finished. Einstein consequently called <math>\Lambda</math> ''"the biggest blunder of my life"''.<ref name="CSR"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Revival of the cosmological constant vs. property of the correct metric== | ||
| + | In general, a positive <math>\Lambda</math> causes acceleration to the universe expansion, whereas negative <math>\Lambda</math> and ordinary matter tend to decelerate it.<ref name="CSR"/> When the ''Supernova Cosmology Project Collaboration'' and ''High-Z Supernova Team Collaboration'' started their research at the beginning of 1990s, both prevailing mainstream cosmological models assumed decelerating universe scenarios. The processing of collected data from research observations however indicated that the universe is accelerating and requires something like non-zero cosmological constant.<ref name="RiessNobel">{{cite web | ||
| + | |author=A.G.Riess | ||
| + | |title=Nobel Prize (in Physics 2011) lecture slides on ''Supernovae Reveal An Accelerating Universe (A Science Adventure Story)'' | ||
| + | |url=http://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&ved=0CCQQFjAA&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.nobelprize.org%2Fnobel_prizes%2Fphysics%2Flaureates%2F2011%2Friess-lecture_slides.pdf&ei=UmtoUOXlN8nXtAahmoCQDw&usg=AFQjCNEJJaEdSL2En2TjIaOTiQ5-Gtz-rQ&sig2=iGSgSzY2T-OO8pj-xAAaEw | ||
| + | }}</ref> The first paper on new discovery was submitted in May 1998<ref>{{cite web | ||
| + | |author=A.G.Riess et al. | ||
| + | |title=Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant | ||
| + | |publisher=Astrophysics | ||
| + | |year=1998 | ||
| + | |url=https://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/9805201 | ||
| + | |iisue=116 | ||
| + | |doi=10.1086/300499 | ||
| + | |pages=1009–1038 | ||
| + | }}</ref> and in December the same year the new discovery of the accelerating universe was declared to be "Breakthrough of the Year" in the journal ''Science''.<ref>{{cite web | ||
| + | |url=http://physicsworld.com/cws/article/news/1998/dec/18/science-chooses-accelerating-universe-as-breakthrough-of-the | ||
| + | |title=Science chooses accelerating universe as "Breakthrough of the Year" | ||
| + | |date=Dec 18, 1998 | ||
| + | |publisher=IOP Publishing, A website from the Institute of Physics, physicsworld.com | ||
| + | |acessdate=4.10.2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | ||
| + | |url=http://www.sciencemag.org/content/282/5397/2156.1 | ||
| + | |title=BREAKTHROUGH OF THE YEAR: ASTRONOMY: Cosmic Motion Revealed | ||
| + | |author=James Glanz | ||
| + | |date=18 December 1998 | ||
| + | |publisher=Science Magazine | ||
| + | |volume=282 | ||
| + | |issue=5397 | ||
| + | |pages=2156–2157 | ||
| + | |doi=10.1126/science.282.5397.2156a | ||
| + | |quote=In 1998, astronomers peered into the universe and found that it is flying apart ever faster, suggesting that Einstein was right when he posited a mysterious energy that fills "empty" space, and in fact that most of the energy of the universe is in this form. Two independent teams of astronomers found that not only is there too little matter in the universe to ever halt the expansion of the universe on its own, but the outward motion appears to be speeding up, not slowing down. At the same time, the finding raises such profound questions about the nature of space that cosmologists are wondering whether the ultimate fate of the universe can ever be known for certain. We therefore name their findings, which transform our view of the universe and pose fundamental new questions for physics, as Breakthrough of the Year for 1998. | ||
| + | |acessdate=7.10.2012}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to [[John Hartnett|J.Hartnett]], it would be fair to state that most cosmologists would like the requirement for cosmological constant to disappear altogether. He interprets its extremely small value as a possible evidence for fine-tuned universe.<ref name="DismantlingBB"/> | ||
| + | The 2011 Nobel Laureate in Physics, Brian P. Schmidt was asked in 2011 the question "what is causing the universe to expand at accelerating rate?" which he answered by words that it is a big mystery why space should have energy at all, people around the world are scratching their heads to figure out but as of today there has not been lot progress yet.<ref>{{cite web | ||
| + | |title=Nobel Laureates 2011 | ||
| + | |publisher=nobelprize.org | ||
| + | |url=https://www.nobelprize.org/mediaplayer/index.php?id=1760 | ||
| + | |accessdate=4.10.2012}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | It has been however declared that [[Moshe Carmeli|Carmeli]]'s theory which has no explicit cosmological constant implies its equivalence of <math>\Lambda</math> = 1.934 × 10<sup>−35</sup> s<sup>−2</sup> and this value is supposed to be in excellent agreement with measurements.<ref name="Cosmological Constant">{{cite web|author=Moshe Carmeli|date=20 November 2002|title=Fundamental Approach to the Cosmological Constant Issue|journal=International Journal of Modern Physics A|volume=17|issue=29|pages=|doi=10.1142/S0217751X02013253|url=http://www.worldscientific.com/doi/abs/10.1142/S0217751X02013253}}</ref> The 'force' pushing the universe apart, which invokes the ideas about [[dark energy]] is more correctly just a property of the correct metric.<ref name="starlight">{{cite book| last = Hartnett| first = John| authorlink = | title = Starlight, Time and the New Physics| publisher = Creation Ministries International| series = | year = 2007| doi = | isbn = 978-0-949-906687|pages=154|quote=}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Notes == | ||
| + | <references group=note/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | {{Reflist}} | ||
| − | [[Category: Cosmology | + | [[Category:Cosmology]] |
| − | + | [[Category:Physics]] | |
| − | [[Category: Physics]] | + | |
Latest revision as of 06:55, April 9, 2019
The Cosmological constant is the constant 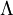 of the Einstein field equation
of the Einstein field equation
 ,
,
where  is Ricci's tensor,
is Ricci's tensor, 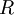 is its contraction,
is its contraction,  is the metric tensor of spacetime,
is the metric tensor of spacetime,  is Newton's constant of gravitation, and
is Newton's constant of gravitation, and 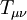 is the stress-energy tensor. (The experimentally derived constant
is the stress-energy tensor. (The experimentally derived constant  has to appear in both Newton's formulation of gravity and the General relativity formulation, since they are compatible.)
has to appear in both Newton's formulation of gravity and the General relativity formulation, since they are compatible.)
Einstein added the cosmological constant term to his gravitational field equations in order to allow the existence of a homogeneous static solutions in the presence of matter, i.e. to make the universe stationary (neither expanding nor contracting). This works when the cosmological constant has the so-called Einstein value:
 ,
,
where  is the mass density of space and
is the mass density of space and  is the speed of light in vacuo.
is the speed of light in vacuo.
Contents
Historical background

In 1915 Einstein introduced the field equation that placed into balance and found equal the curvature at one side and mass on the other. He hoped that the equations of general relativity would determine a single universe model without any beginning or end. For reasons he could never make clear, he found universe so conceived particularly satisfying and he managed to find a solution to his own equations that specified universe of that sort, static and unchanged forever.[2][note 1] A.G. Riess declares that Einstein's original idea was to have constant amount of energy in the space.[4] When in 1920s Russian mathematician A.Friedman (1924)[5] and Belgian catholic priest and professor of physics G.Lemaître (1927)[6] independently found that Einstein's gravitational field equations of general relativity have non-static cosmological solution[2] implying an expanding or collapsing universe,[7] Einstein, wishing to cancel out expansion, suggested modification to his field equations by adding a so-called cosmological term.[8] [note 2] Before long, after Hubble's interpretation of new discoveries as expanding universe in 1929, the role of cosmological constant aiming to allow static homogeneous solutions to field equations in presence of matter seemed finished. Einstein consequently called 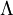 "the biggest blunder of my life".[8]
"the biggest blunder of my life".[8]
Revival of the cosmological constant vs. property of the correct metric
In general, a positive 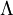 causes acceleration to the universe expansion, whereas negative
causes acceleration to the universe expansion, whereas negative 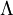 and ordinary matter tend to decelerate it.[8] When the Supernova Cosmology Project Collaboration and High-Z Supernova Team Collaboration started their research at the beginning of 1990s, both prevailing mainstream cosmological models assumed decelerating universe scenarios. The processing of collected data from research observations however indicated that the universe is accelerating and requires something like non-zero cosmological constant.[4] The first paper on new discovery was submitted in May 1998[9] and in December the same year the new discovery of the accelerating universe was declared to be "Breakthrough of the Year" in the journal Science.[10][11]
and ordinary matter tend to decelerate it.[8] When the Supernova Cosmology Project Collaboration and High-Z Supernova Team Collaboration started their research at the beginning of 1990s, both prevailing mainstream cosmological models assumed decelerating universe scenarios. The processing of collected data from research observations however indicated that the universe is accelerating and requires something like non-zero cosmological constant.[4] The first paper on new discovery was submitted in May 1998[9] and in December the same year the new discovery of the accelerating universe was declared to be "Breakthrough of the Year" in the journal Science.[10][11]
According to J.Hartnett, it would be fair to state that most cosmologists would like the requirement for cosmological constant to disappear altogether. He interprets its extremely small value as a possible evidence for fine-tuned universe.[7] The 2011 Nobel Laureate in Physics, Brian P. Schmidt was asked in 2011 the question "what is causing the universe to expand at accelerating rate?" which he answered by words that it is a big mystery why space should have energy at all, people around the world are scratching their heads to figure out but as of today there has not been lot progress yet.[12]
It has been however declared that Carmeli's theory which has no explicit cosmological constant implies its equivalence of 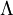 = 1.934 × 10−35 s−2 and this value is supposed to be in excellent agreement with measurements.[13] The 'force' pushing the universe apart, which invokes the ideas about dark energy is more correctly just a property of the correct metric.[14]
= 1.934 × 10−35 s−2 and this value is supposed to be in excellent agreement with measurements.[13] The 'force' pushing the universe apart, which invokes the ideas about dark energy is more correctly just a property of the correct metric.[14]
Notes
- ↑ The contemporary atheistic scientists such as S.Hawking believe there is no room for creator in the universe which has no boundary or edge whereas in universe which had beginning we could suppose it had a creator.[3] See also: Antipathy to the idea of beginning
- ↑ cf."the 'cosmological constant' ... [also] had the effect of balancing the gravitational attraction that would otherwise cause the universe to collapse"[3]
References
- ↑ Isaacson, Walter (2008). Einstein: His Life and Universe (New York: Simon and Schuster), p. 390. Retrieved from GoogleBooks archive on February 19, 2015.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 David Berlinski. "The Cause", The Devil’s Delusion. Basic Books, New York, 2009, 77. ISBN 978-0-465-01937-3.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Edgar Anrews (2010). Who made God? Searching for a theory of everything.. Carlisle, PA, USA: EP Books, 98, 100. ISBN 978-0-85234-707-2. “Stephen Hawking puts it thus: 'So long as the universe had a beginning, we could suppose it had a creator. But if universe is really completely self-contained, having no boundary or edge, it would have neither beginning not end; it would simply be. What place then for creator?'”
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 A.G.Riess. Nobel Prize (in Physics 2011) lecture slides on Supernovae Reveal An Accelerating Universe (A Science Adventure Story).
- ↑ Alexander Friedmann. Über die Möglichkeit einer Welt mit konstanter negativer Krümmung des Raumes (German) 326–332. Zeitschrift für Physik. DOI:10.1007/BF01328280.
- ↑ G. Lemaître (April 1927). Un Univers homogène de masse constante et de rayon croissant rendant compte de la vitesse radiale des nébuleuses extra-galactiques (French).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Alex Williams, John Hartnett (2005). Dismantling the Big Bang. Green Forest, AR, USA: Master Books, 110. ISBN 978-0-89051-437-5. “...his equations were telling [Einstein] that [the universe] had to be either collapsing or expanding...A large value [of cosmological constant] would cause large redshifts and spacial distortion in nearby objects...[the cosmological constant ...involves fine-tuning of over 120 orders of magnitude (quoted Lawrence Krauss)]”
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Moshe Carmeli (2002). Cosmological Special Relativity, The Large-Scale Structure of Space, Time and Velocity, 2nd Edition. World Scientific Publishing, 2, 168. ISBN 9-789-02-4936-5.
- ↑ A.G.Riess et al. (1998). Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant 1009–1038. Astrophysics. DOI:10.1086/300499.
- ↑ Science chooses accelerating universe as "Breakthrough of the Year". IOP Publishing, A website from the Institute of Physics, physicsworld.com (Dec 18, 1998).
- ↑ James Glanz (18 December 1998). BREAKTHROUGH OF THE YEAR: ASTRONOMY: Cosmic Motion Revealed 2156–2157. Science Magazine. DOI:10.1126/science.282.5397.2156a. “In 1998, astronomers peered into the universe and found that it is flying apart ever faster, suggesting that Einstein was right when he posited a mysterious energy that fills "empty" space, and in fact that most of the energy of the universe is in this form. Two independent teams of astronomers found that not only is there too little matter in the universe to ever halt the expansion of the universe on its own, but the outward motion appears to be speeding up, not slowing down. At the same time, the finding raises such profound questions about the nature of space that cosmologists are wondering whether the ultimate fate of the universe can ever be known for certain. We therefore name their findings, which transform our view of the universe and pose fundamental new questions for physics, as Breakthrough of the Year for 1998.”
- ↑ Nobel Laureates 2011. nobelprize.org. Retrieved on 4.10.2012.
- ↑ Moshe Carmeli (20 November 2002). Fundamental Approach to the Cosmological Constant Issue. DOI:10.1142/S0217751X02013253.
- ↑ Hartnett, John (2007). Starlight, Time and the New Physics. Creation Ministries International, 154. ISBN 978-0-949-906687.