Hamiltonian
The Hamiltonian is a quantity of great importance in both classical and quantum mechanics.
Classical mechanics
In classical dynamics, the Hamiltonian is defined to be

where  are the generalised coordinates and
are the generalised coordinates and 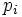 are the momenta conjugate to these coordinates, and
are the momenta conjugate to these coordinates, and 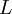 is the Lagrangian. For many problems the Hamiltonian is the same as the energy.
is the Lagrangian. For many problems the Hamiltonian is the same as the energy.
Example
For a mass  attached to a spring of spring constant
attached to a spring of spring constant  extended by a distance
extended by a distance  ,
,  and so
and so

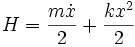
which is the familiar expression for the energy of a simple harmonic oscillator.
Quantum mechanics
The Hamiltonian for many quantum mechanical systems can be obtained by writing down a corresponding classical Hamiltonian and promoting all of the coordinates and momenta to operators. The quantum mechanical Hamiltonian is of central importance to the Schrodinger equation.