Difference between revisions of "Absolute value"
m (→ref: there were none, removed section) |
m (Added categories) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[Complex number]]s also have an absolute value. If <math>z = x+iy</math> is a complex number with real part <math>x</math> and imaginary part <math>y</math>, then <math>|z| = \sqrt{x^2 + y^2}</math>. If we represent <math>z</math> as a point in the complex plane with coordinates <math>(x,y)</math>, then <math>|z|</math> is the distance from this point to the origin. The absolute value of complex numbers also has the multiplicative property and satisfies the triangle inequality. | [[Complex number]]s also have an absolute value. If <math>z = x+iy</math> is a complex number with real part <math>x</math> and imaginary part <math>y</math>, then <math>|z| = \sqrt{x^2 + y^2}</math>. If we represent <math>z</math> as a point in the complex plane with coordinates <math>(x,y)</math>, then <math>|z|</math> is the distance from this point to the origin. The absolute value of complex numbers also has the multiplicative property and satisfies the triangle inequality. | ||
| + | [[Category:Algebra Terms]] | ||
[[Category:Algebra]] | [[Category:Algebra]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Mathematics]] | ||
Revision as of 04:43, March 16, 2011
The absolute value of a number is a measure of the size of that number. The absolute value of  is written
is written  .
.
- If
 is a positive number, then
is a positive number, then  .
.
- If
 is a negative number, then
is a negative number, then  .
.
- If
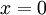 then
then  .
.
Absolute value has several useful properties. One is the multiplicative property. If  and
and  are two numbers, then
are two numbers, then  . Another is the triangle inequality, which is the fact that
. Another is the triangle inequality, which is the fact that 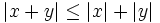 . For example, if
. For example, if 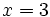 and
and  , then
, then  , while
, while  . In this case, the triangle inequality is the fact that 2 is not more than 8.
. In this case, the triangle inequality is the fact that 2 is not more than 8.
Complex numbers also have an absolute value. If 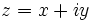 is a complex number with real part
is a complex number with real part  and imaginary part
and imaginary part  , then
, then 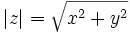 . If we represent
. If we represent  as a point in the complex plane with coordinates
as a point in the complex plane with coordinates  , then
, then 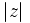 is the distance from this point to the origin. The absolute value of complex numbers also has the multiplicative property and satisfies the triangle inequality.
is the distance from this point to the origin. The absolute value of complex numbers also has the multiplicative property and satisfies the triangle inequality.