Coriolis force
The Coriolis force is one of three fictitious forces that act in rotating frames of reference such as the earth.[1] It is fictitious in the sense that it does not derive from a physical force such as gravity or electromagnetism. While Newton's laws of motion are strictly only valid in inertial (non-accelerating) frames of reference, by including fictitious forces such as the Coriolis force as additional forces Newton's second law can be used to describe the motion of objects when viewed from rotating reference frames. A commonly given example of the Coriolis force in action is how hurricanes in the Northern hemisphere rotate counterclockwise while cyclones and typhoons in the Southern hemisphere rotate clockwise.[2] The other two fictitious forces that exist in rotating frames are the centrifugal and Euler forces.
Mathematics
The acceleration of an object due to the Coriolis force, ac can be described mathematically by:
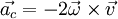
where ω is the angular velocity of the rotating reference frame and v is the velocity of the object when viewed from an inertial frame of reference (non-accelerating). The cross product means that the Coriolis force acts at right angles to both the velocity of the object and angular velocity of the reference frame. This can be used to explain the rotation directions of hurricanes, cyclones and typhoons. On earth, the angular velocity vector points up out of the North pole. Supposing the wind is blowing from the South in the Northern hemisphere, the Coriolis force will act to bend it to the right when viewed from above. This means tropical storms in the Northern hemisphere (hurricanes) will rotate counterclockwise. Similarly in the Southern hemisphere and air current travelling South will be bent to the left and so cyclones and typhoons in the Southern hemisphere will rotate clockwise. The deflection of something by the Coriolis force is known as the Coriolis effect.